BFS의 가장 기초인 최단거리 구하기문제!
이 문제를 통해서 최단거리 구할때는 BFS가 유리하다는 것을 깨닫게 되었습니다!
일단 문제 풀기
1. 문제
N×M크기의 배열로 표현되는 미로가 있다.
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
미로에서 1은 이동할 수 있는 칸을 나타내고, 0은 이동할 수 없는 칸을 나타낸다. 이러한 미로가 주어졌을 때, (1, 1)에서 출발하여 (N, M)의 위치로 이동할 때 지나야 하는 최소의 칸 수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. 한 칸에서 다른 칸으로 이동할 때, 서로 인접한 칸으로만 이동할 수 있다.
위의 예에서는 15칸을 지나야 (N, M)의 위치로 이동할 수 있다. 칸을 셀 때에는 시작 위치와 도착 위치도 포함한다.
입력
첫째 줄에 두 정수 N, M(2 ≤ N, M ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 M개의 정수로 미로가 주어진다. 각각의 수들은 붙어서 입력으로 주어진다.
출력
첫째 줄에 지나야 하는 최소의 칸 수를 출력한다. 항상 도착위치로 이동할 수 있는 경우만 입력으로 주어진다.
2. 코드 구현
package java_BFS_DFS_basic;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
class location{
int w,h,num;
location(int h, int w,int num){
this.h = h;
this.w = w;
this.num = num;
}
}
public class findMinPath {
static Queue<location> q = new LinkedList<location>();
static Stack<location> s = new Stack<location>();
public static void findPath_dfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] ck,int sum) {
location start;
while(!s.isEmpty()) {
start = s.peek();
map[start.h][start.w] = start.num;
s.pop();
//아래로 이동
if(start.h+1 < map.length && !ck[start.h+1][start.w] && map[start.h+1][start.w] !=0) {
s.push(new location(start.h+1,start.w,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h+1][start.w] = true;
}
//오른쪽 이동
if(start.w+1 < map[start.h].length && !ck[start.h][start.w+1] && map[start.h][start.w+1] !=0) {
s.push(new location(start.h,start.w+1,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h][start.w+1] = true;
}
//왼쪽 이동
if(start.w-1 >= 0 && !ck[start.h][start.w-1] && map[start.h][start.w-1] !=0) {
s.push(new location(start.h,start.w-1,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h][start.w-1] = true;
}
//위로 이동
if(start.h-1 >= 0 && !ck[start.h-1][start.w] && map[start.h-1][start.w] != 0) {
s.push(new location(start.h-1,start.w,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h-1][start.w] = true;
}
}
}
public static void findPath_bfs(int[][] map, boolean[][] ck,int sum) {
location start;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
start = q.peek();
map[start.h][start.w] = start.num;
q.poll();
//아래로 이동
if(start.h+1 < map.length && !ck[start.h+1][start.w] && map[start.h+1][start.w] !=0) {
q.add(new location(start.h+1,start.w,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h+1][start.w] = true;
}
//오른쪽 이동
if(start.w+1 < map[start.h].length && !ck[start.h][start.w+1] && map[start.h][start.w+1] !=0) {
q.add(new location(start.h,start.w+1,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h][start.w+1] = true;
}
//왼쪽 이동
if(start.w-1 >= 0 && !ck[start.h][start.w-1] && map[start.h][start.w-1] !=0) {
q.add(new location(start.h,start.w-1,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h][start.w-1] = true;
}
//위로 이동
if(start.h-1 >= 0 && !ck[start.h-1][start.w] && map[start.h-1][start.w] != 0) {
q.add(new location(start.h-1,start.w,map[start.h][start.w]+1));
ck[start.h-1][start.w] = true;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//int[][] map = {{1,1,1,1},{0,0,1,0},{1,1,1,0},{0,0,1,2}};
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n,m;
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
String[] temp = new String[n];
int map[][] = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
temp[i] = sc.next();
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
map[i][j]=Integer.parseInt(temp[i].substring(j, j+1));
}
}
boolean[][] ck = new boolean[n][m];
/*DFS 탐색*/
//s.push(new location(0,0,1));
//ck[0][0] = true;
//findPath_dfs(map,ck,1);
/*BFS 탐색*/
q.add(new location(0,0,1));
ck[0][0] = true;
findPath_bfs(map,ck,1);
System.out.println(map[n-1][m-1]);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
3. 문제 풀이
이 문제를 보면 왜 BFS가 최단거리 탐색에 유리한지 알 수 있습니다.
그림을 볼 필요도 없이..
최단거리에 BFS가 유리한 이유는 사실 DFS는 한 방향만 있는힘껏 탐색하기 때문입니다.
아래 그림과 같은 문제가 있다고 가정하겠습니다.

3-1. BFS 탐색
먼저 BFS 탐색을 보겠습니다.
BFS는 큐(Queue)로 구성되어 있기 때문에 분기점으로 나누어져도 분할된 채로 한칸씩 이동합니다.
(1,0) 지점에서 2갈래 길로 나누어지는 시점에서 큐의 상태를 보겠습니다.

위 그림과 같이 코드에 작성했던 순서대로 아래->오른쪽 탐색을 통해 (2,0)과 (1,1) 두개가 큐에 삽입 됩니다.
그 다음 poll 값 2,0에서 탐색을 진행합니다.
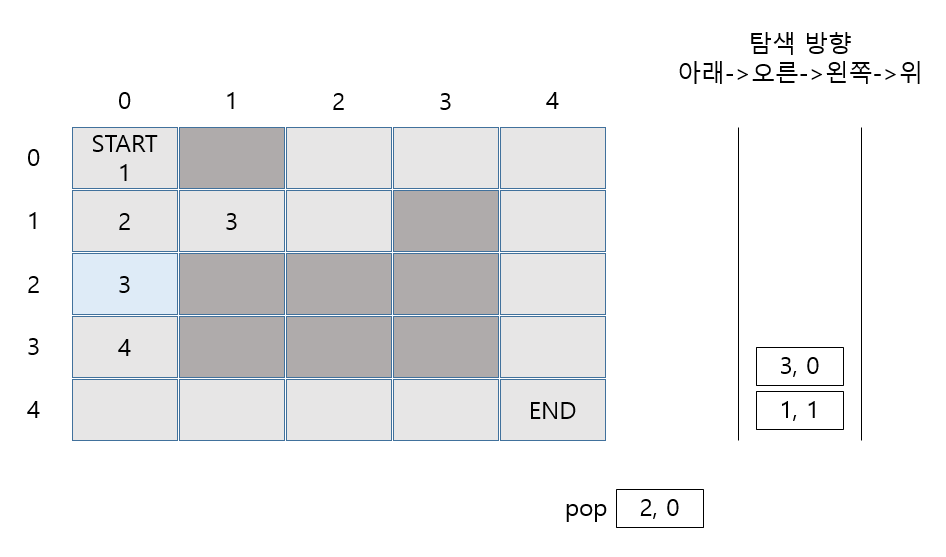
(2,0)에서는 (3,0)만 갈 수 있으므로, 큐에 (3,0)을 삽입 후 다음으로 진행합니다.
그 다음 poll 값은 (1,1) 입니다.

(1,1)에서 갈 수 있는 길은 (1,2)뿐 이므로 (1,2)를 큐에 삽입합니다.
이런식으로 동작하기 때문에 BFS는 분할 되어도 하나씩 진행이 가능한 것이죠.
3-2. DFS 탐색
같은 시점 DFS의 상태를 보겠습니다.
DFS는 스택으로 구현되기 때문에 아래 그림과 같이 동작합니다.

마찬가지로 (1,0)에서 갈 수 있는 2가지 길 모두 Stack에 Push 합니다.
설정한 탐색 순서에 따라 (2,0), (1,0)을 삽입 합니다.
그 다음 하나를 pop을 합니다.

(1,1)에서 갈 수 있는 (1,2)를 stack에 push 합니다.
그리고 하나를 pop 합니다.

이렇듯 DFS 탐색은 한쪽 길을 끝까지 탐색합니다.
4. 결과
결과적으로 BFS/DFS 탐색은 아래 그림과 같은 결과를 보여줍니다.

위 결과에서 보여주듯이 DFS 탐색은 한 방향을 쭉 탐색하기 최소 거리 구하기에는 적합하지 않습니다.
그래서 최소거리를 구할땐 BFS를 사용하는 것이죠!
'알고리즘 공부 > 알고리즘 문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 트리 dfs 탐색 (0) | 2021.04.23 |
|---|---|
| 나누어 떨어지는 숫자 배열 (0) | 2019.03.12 |
| 문자열 내 맘대로 정렬하기 (0) | 2019.03.12 |
| 빙고 개수 카운트하기 (0) | 2019.01.31 |
| 배열 회전 결과값 확인하기 (1) | 2019.01.26 |